
Chlorine has 7 electrons in its valence shell. It can acquire stable configuration (2, 8, 8) of nearest inert gas (Ar) by gaining one electron (lost by sodium) and forming a negative ion (anion) of chlorine. Sodium and chlorine ions alone have a very strong bond, but as soon as you put those ions in a solution with H+, OH-, F- or Mg++ ions, there are charged. It can acquire stable configuration (2, 8) of nearest inert gas (Ne) by losing one electron and forming a positive ion (cation) of sodium. Sodium has one electron in its valence shell. (2, 8, 1) while that of chlorine Cl (Z = 17) is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 5 i.e. Example of Ionic Bond A classic example of ionic bonding is. Thus an ionic or electrovalent bond is defined as a bond between two atoms is the electrostatic force of attraction which holds together the ions of combining atoms formed by the complete transfer of one or more electrons from the electropositive to the electronegative atom.Įlectronic configuration of sodium Na (Z = 11) is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1 i.e. Ionic Bonds An Ionic bond is when an electron leaves one atom and exothermically enters into. When atoms lose electrons they become positive. The oppositely charged formed ions are bound together by electrostatic attraction between them. Atoms lose or gain electrons to attain a complete outer shell of electrons. Thus an ionic bond is formed between metallic and non-metallic atom. Generally, metals are electropositive and nonmetals are electronegative. The atom which acquires electrons is called an electronegative element and accepting electron it forms a negative ion called an anion. Mixtures contain different elements or compounds that can be separated.
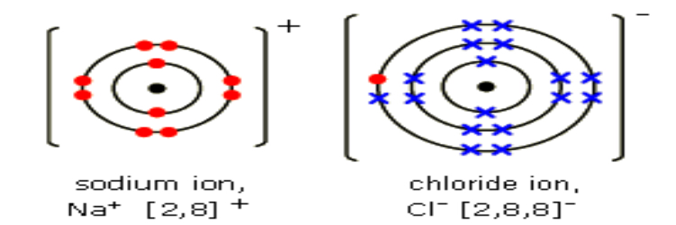

The atom which loses electrons is called an electropositive element and losing electron it forms a positive ion called a cation. A compound is a substance which contains two or more types of atom bonded together. This bond is formed between two atoms whose electronegativity difference is large and they can attain octets by the complete transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
